Project Management
AgentScope-Studio provides powerful project management capabilities to help you visually manage your AgentScope projects. Through the organizational structure of Projects and Runs, you can clearly separate and manage your observability data.
Concepts
In AgentScope-Studio, a Project contains multiple Runs. Specifically:
- Projects: Used to organize and isolate different AI applications or experiments
- Runs: Individual execution instances within a project, similar to sessions, tracking a complete running process
Project Management
The Projects page in AgentScope-Studio provides an overview and management functionality for running projects:
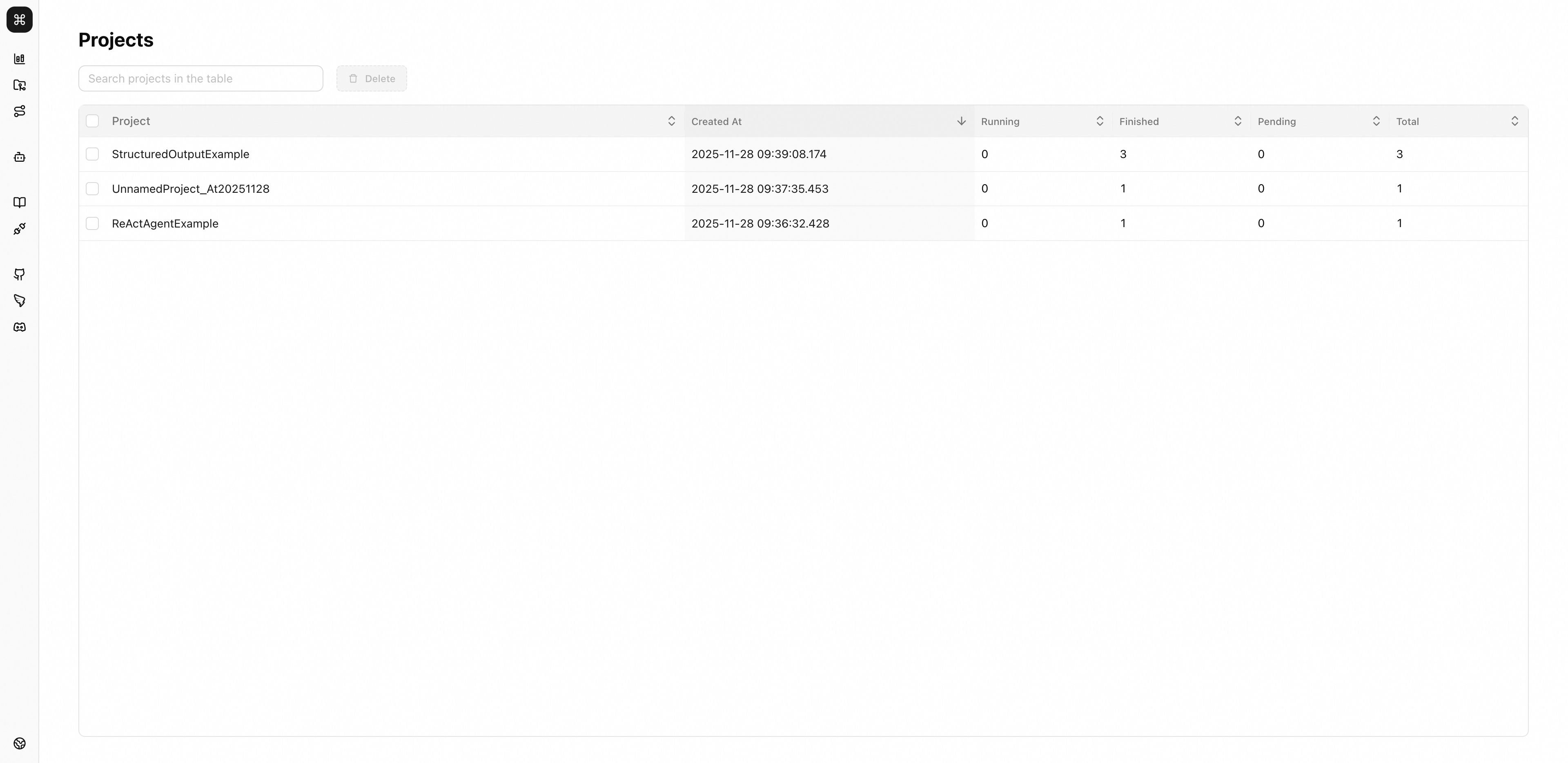
Click on any project in the project list to enter the run management interface and view all run instances under that project.
Run Instance Management
Run Visualization
Run instances contain complete execution tracking and status monitoring functionality. In the (left) sidebar, all run instances under the project are stacked in chronological order. Click on any run instance to view its complete interaction history and status in a Chatbot-style UI. In addition, the right panel provides detailed information and statistics for that run.
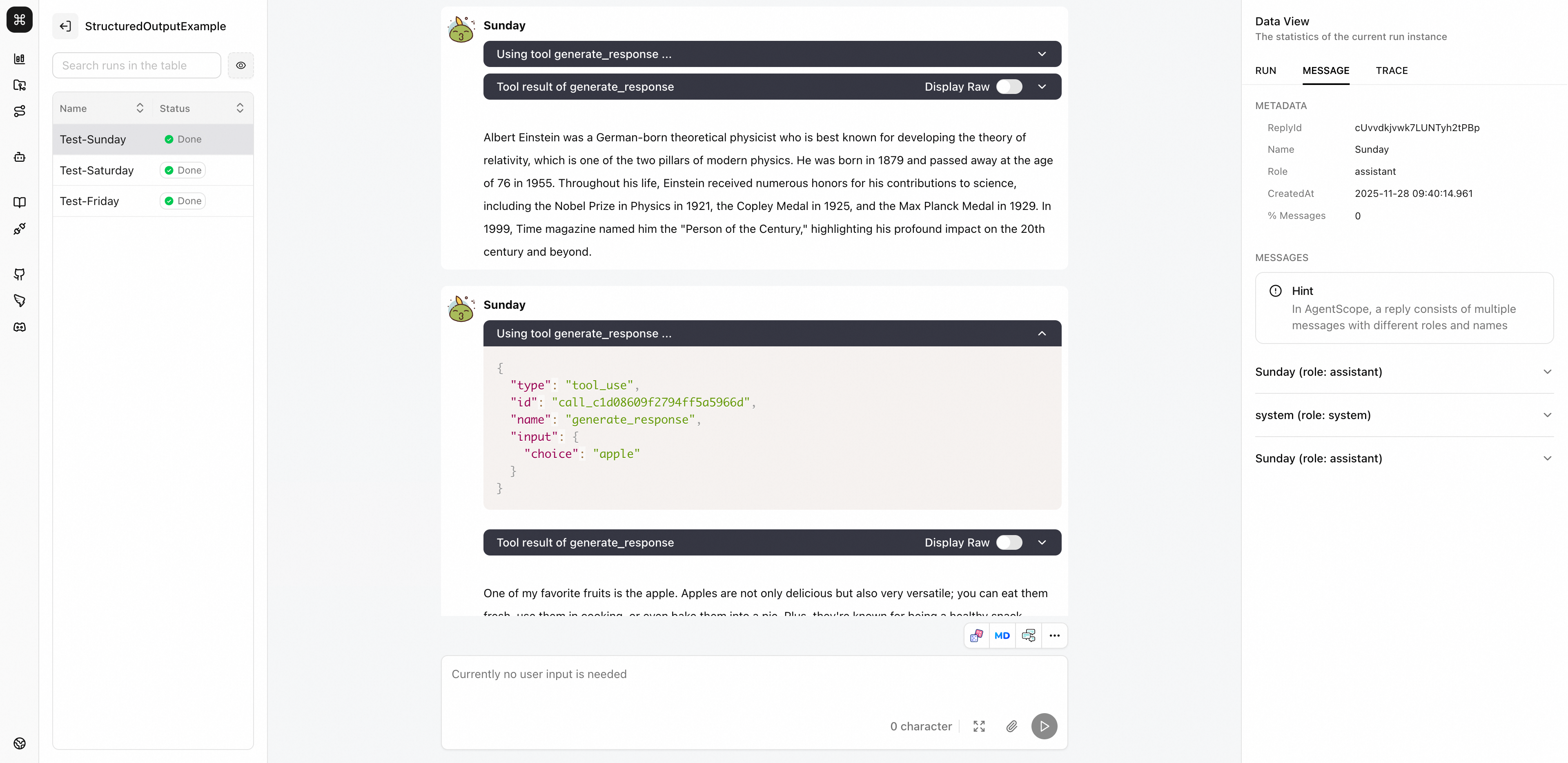
In AgentScope, a single agent reply (i.e., calling the reply function once) generates multiple messages (Msg objects). These messages may be prompt messages to guide the LLM (with role "user"), or tool execution results (with role "system").
Therefore, at the visualization level, we introduce the concept of reply above the message level to organize multiple messages together into a complete agent reply unit. In the run visualization interface, developers can choose to view messages by replyId or msg.id.
User Input Hosting
When an AgentScope project connects to Studio, Studio automatically hosts user input and pushes it in real-time to the Python agent application via WebSocket. Studio also supports multiple different UserAgent instances within a single run instance, enabling multi-user collaborative interaction scenarios.
Run Trace Visualization
AgentScope-Studio also provides OpenTelemetry-based trace data visualization in the right panel, helping developers understand detailed inputs and outputs of agent objects, LLM calls, tool usage, and other components during each run.
API Protocol
The API protocols related to project management in AgentScope-Studio are as follows:
Note: For detailed information about Trace data format, push mechanism, and integration examples, please refer to the Trace documentation.
| Function | Endpoint | Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Register Run | /trpc/registerRun | POST | Register a new Agent run instance |
| Push Message | /trpc/pushMessage | POST | Send Agent messages to the Web interface |
| Request User Input | /trpc/requestUserInput | POST | Agent actively requests user input |
1. Register Run Protocol
Register a run instance on Studio.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
id | string | ✓ | Run instance ID |
project | string | ✓ | Project name |
name | string | ✓ | Run instance name |
timestamp | string | ✓ | ISO timestamp |
pid | number | ✓ | Process ID |
status | enum | ✓ | Run status (e.g., "running", "finished", "error") |
2. Message Push Protocol
Send Msg objects to Studio for display.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
runId | string | ✓ | Run instance ID |
replyId | string | ✓ | Reply message ID |
replyName | string | ✓ | Name of the replier |
replyRole | string | ✓ | Role of the replier (e.g., "assistant", "user") |
msg.id | string | ✓ | Message ID |
msg.name | string | ✓ | Message sender name |
msg.role | string | ✓ | Message sender role (e.g., "assistant", "user", "system") |
msg.content | ContentBlocks | ✓ | Message content |
msg.metadata | object | ✓ | Message metadata |
msg.timestamp | string | ✓ | Message ISO timestamp |
ContentBlocks Format:
ContentBlocks is an array of content blocks. Each block has a type field that determines its structure. Supported content block types include:
- Text Block (
type: "text"): Contains atextfield storing message content - Thinking Block (
type: "thinking"): Contains athinkingfield storing reasoning content - Image Block (
type: "image"): Contains asourcefield, can be base64 data or URL - Audio Block (
type: "audio"): Contains asourcefield, can be base64 data or URL - Video Block (
type: "video"): Contains asourcefield, can be base64 data or URL - Tool Use Block (
type: "tool_use"): Containsid,name, andinputfields - Tool Result Block (
type: "tool_result"): Containsid,name, andoutputfields
For media blocks (image, audio, video), source can be:
- Base64 Source:
{ type: "base64", media_type: string, data: string } - URL Source:
{ type: "url", url: string }
Example:
content_blocks = [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "Greetings from your agent!"
},
{
"type": "image",
"source": {
"type": "base64",
"media_type": "image/jpeg",
"data": "data:image/jpeg;base64,/9j/4AAQSkZJRg..."
}
},
{
"type": "tool_use",
"id": "tool-123",
"name": "search",
"input": {"query": "weather"}
}
]3. User Input Protocol
Request user input on the Studio frontend page with a specific role/name/identity.
Request Fields:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
requestId | string | ✓ | User input request ID |
runId | string | ✓ | Run instance ID |
agentId | string | ✓ | Agent ID |
agentName | string | ✓ | Agent name |
structuredInput | object | JSON Schema for structured input form |
The specific implementation logic for user input involves multi-party interaction between the Python application, Studio server, and frontend. Below is the detailed interaction flow:
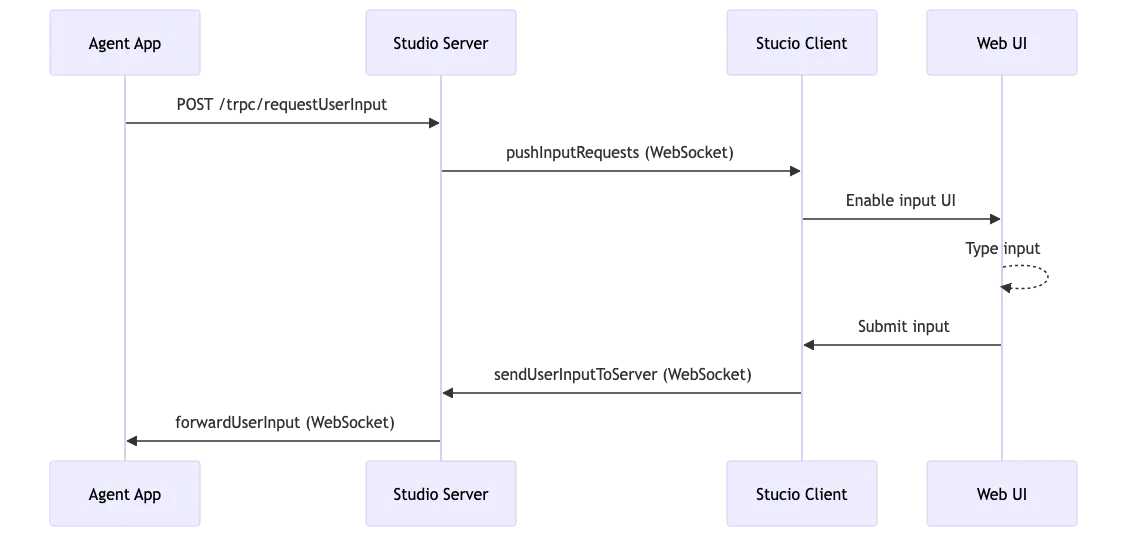
- Agent Sends Request: The Agent sends a user input request to the Studio server via POST request
- Server Saves Request: The Studio server saves the request to the database and pushes it to the Web client via WebSocket
- User Input: The user enters content in the Web interface
- Client Sends: The Web client sends the user input back to the server via WebSocket
- Server Forwards: The server validates and forwards the user input to the Agent's WebSocket connection
- Agent Receives: The Agent receives the user input via WebSocket and continues execution
Integration Example
The following example demonstrates how to integrate project management-related protocols:
from agentscope.message import Msg
from datetime import datetime
from queue import Queue
from threading import Event
from typing import Any, List
import requests
import shortuuid
import socketio
class StudioClient:
"""Complete Studio client for custom Agent integration"""
def __init__(self, studio_url: str):
self.studio_url = studio_url
self.sio = socketio.Client()
self.input_queues = {}
self.input_events = {}
def register_run(
self,
id: str,
project: str,
name: str,
timestamp: str,
pid: int,
status: str,
) -> None:
"""Register a run instance"""
response = requests.post(
f"{self.studio_url}/trpc/registerRun",
json={
"id": id,
"project": project,
"name": name,
"timestamp": timestamp,
"pid": pid,
"status": status,
},
timeout=10
)
response.raise_for_status()
# Connect WebSocket to receive user input
self.sio.connect(
self.studio_url,
namespaces=["/python"],
auth={"run_id": id}
)
# Listen for user input
@self.sio.on("forwardUserInput", namespace="/python")
def receive_user_input(
request_id: str,
blocks_input: List[dict],
structured_input: dict[str, Any],
) -> None:
if request_id in self.input_queues:
self.input_queues[request_id].put({
"blocks_input": blocks_input,
"structured_input": structured_input,
})
self.input_events[request_id].set()
def push_message(
self,
run_id: str,
reply_id: str,
reply_name: str,
reply_role: str,
msg: Msg
) -> None:
"""Push message to Studio"""
payload = {
"runId": run_id,
"replyId": reply_id,
"replyName": reply_name,
"replyRole": reply_role,
"msg": msg.to_dict()
}
response = requests.post(
f"{self.studio_url}/trpc/pushMessage",
json=payload,
timeout=10
)
response.raise_for_status()
def request_user_input(self, run_id: str, agent_id: str, agent_name: str,
structured_input=None):
"""Request user input from Studio"""
request_id = shortuuid.uuid()
self.input_queues[request_id] = Queue()
self.input_events[request_id] = Event()
try:
response = requests.post(
f"{self.studio_url}/trpc/requestUserInput",
json={
"requestId": request_id,
"runId": run_id,
"agentId": agent_id,
"agentName": agent_name,
"structuredInput": structured_input
},
timeout=10
)
response.raise_for_status()
# Wait for user response
self.input_events[request_id].wait(timeout=300)
if request_id in self.input_queues:
return self.input_queues[request_id].get()
else:
raise TimeoutError("User input timeout")
finally:
# Cleanup
if request_id in self.input_queues:
del self.input_queues[request_id]
if request_id in self.input_events:
del self.input_events[request_id]
# Usage example
client = StudioClient("http://localhost:3000")
# Register run
client.register_run(
id="run-12345",
project="my-project",
name="custom-agent",
timestamp=datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"),
pid=12345,
status="running"
)
# Create a prompt message
msg = Msg("my-agent", "<system-hint>You should now...</system-hint>", "user")
# Push message
client.push_message(
run_id="run-12345",
reply_id="reply-1",
reply_name="my-agent",
reply_role="assistant",
msg=msg
)
# Request user input
user_response = client.request_user_input(
run_id="run-12345",
agent_id="agent-1",
agent_name="My Agent"
)
print(f"User responded: {user_response}")